5G brings hope of brighter days ahead but requires data infrastructure that keeps up
The telecom industry digital transformation imperative
Several market forces have combined to drive sector wide digital transformation of communications service providers globally, aka the telecom industry. Digital transformation is generally a thumbnail description of diverse range of digital investment and process changes to generate business outcomes of cost reduction, increasing CX, increasingly agility, and increasingly overall intelligence.
Telecom operators need help in all these areas as topline revenue growth has slowed or disappeared completely while overall network utilization continues to go up. To address the revenue growth challenge, many operators are looking beyond their core voice, fixed, and wireless broadband services to seek more profitable and durable value chain positions, especially in areas like enterprise services but also with consumers. This transition “up the stack” can be described as the transition from communication service providers to digital service providers. Telecom operators seek to increase their overall service agility and velocity and are eager to take on more responsibility for innovation by adopting emerging IT practices such as DevOps and CI/CD.
To address the network utilization challenge in core services they require solutions that drastically reduce the CAPEX and OPEX costs to deliver core network services. One of the key levers they must address network costs is cloudification which describes the transition from network appliances to network functions delivered as software using cloud-like infrastructure models. The goal is to achieve a level of openness in the core network to alleviate single vendor control points such as the work underway in Open RAN.
As part of their transformation they seek creative ways to collectively harness the power of the customer profile, billing, service utilization, network traffic, and even external day to solve practical challenges like fraud management and real-time charging, to achieving better revenue management and marketing personalization. On the network side the status quo will not sustain much longer, a step-change is required in overall system automation and efficiency, again to begin to approach what has been achieved by public cloud providers. In all these areas it is expected that artificial intelligence/machine learning and advanced data management techniques will be foundational given the scale on which telcos operate.
Raising it overall intelligence by harnessing its troves of data is even more vital as improving its customer facing experience delivered via digital channels. The goal is achieving a 360-degree view of the customer to the end of elevating customer experience and automating as much as possible including upsells and first line customer support. These outcomes have become vital as consumers are demanding experience parity with what companies like Netflix, Facebook, Amazon, and Google are able to deliver while enterprises seek solutions are par with the best in public cloud service and SaaS.
While this all might paint a picture that would appear wrought with challenges there is significant reason for optimism for the years ahead. First, the mission critical role of the telecom industry was re-enforced by the global COVID-19 pandemic. As the world transitioned overnight to WFH and social distancing drove us away from interpersonal interaction our broadband services became a vital lifeline to the outside world which allowed many to continue to work, learn, and be entertained. It is for this reason that the telecom sector has proven to be resilient when compared to other vertical markets like travel, retail and hospitality. In addition, the telecom industry has an ace up their sleeve named 5G and its revolutionary performance, cloud-native architecture and distributed topology, and value-added service potential with consumers and especially enterprise will be game-changing.
5G to the rescue?
5G is the fifth generation of wireless cellular technology, which has evolved over the past forty years from 1-4G (LTE) with each step-change averaging a decade in duration. 5G is the first network evolution that specifies extensive use of disaggregated, virtualized network functions and cloud-native technologies in architecture design and a highly distributed physical topology to make use of high band spectrum [millimeter wave] to support 100X bandwidth performance and edge computing to support ultra-reliable, low latency application [URLLC] services. These distributed computing will open opportunities around multi-access edge (MEC) computing that include allowing telecom operators to compete for cloud workloads best executed at the edge, collaborate directly with cloud providers for joint value creation, and open platform business models.
Once 5G standards are fully commercialized 5G operators will be able to dynamically create virtual slices of a single physical network deployment to concurrently serving broadband, low-latency, and massive IOT use cases. All this together positions 5G as a ‘game-changer’ for network performance and application experiences opening the door to new value chain positions and revenue pools for 5G network builders. 5G readily supports the digital transformation of a diverse mix of vertical industries like manufacturing, gaming, military, transportation, healthcare, and retail. Workloads well suited for 5G capabilities include predictive maintenance, remote control applications, robotics, autonomous vehicles and robots, drones, AR/VR, and support for massive IoT deployments.
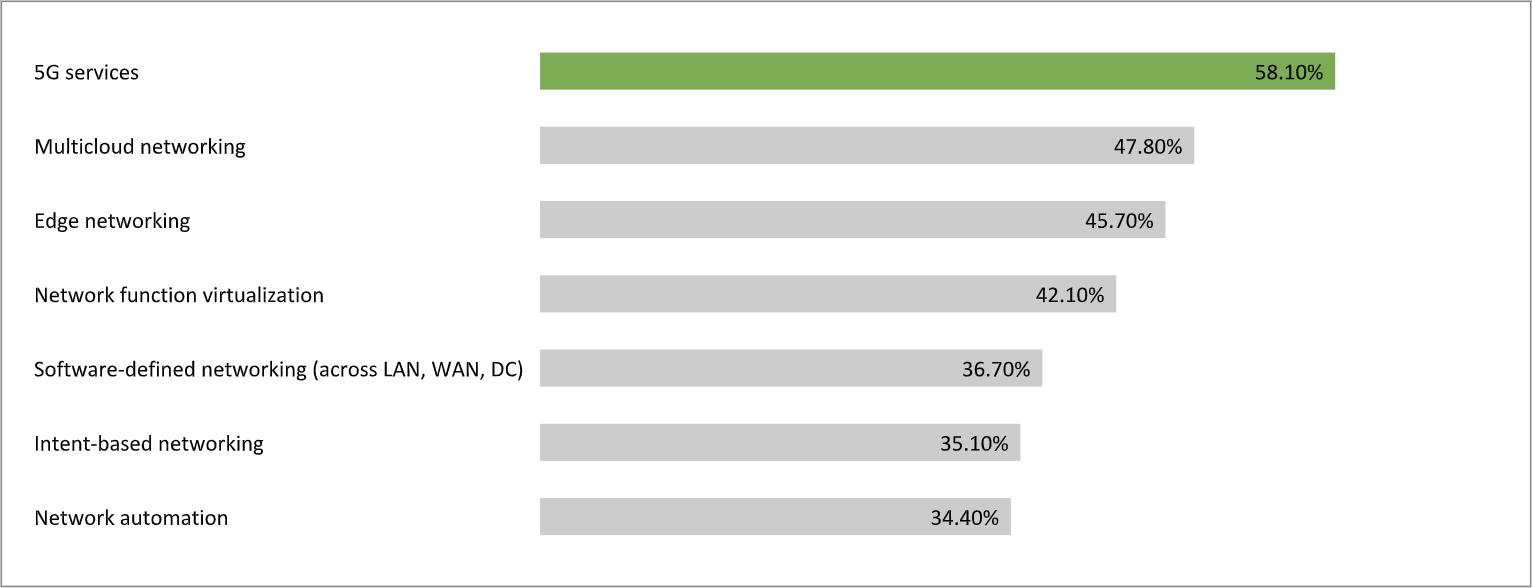
Expectations for 5G are very high as we can see in Figure 1 where 5G was #1 highest network innovation in support of digital transformation objectives.
Figure 1.
Q/Which of the following technologies are most critical to supporting your digital transformation objectives? N=387, Source: 451 Research custom study done for IBM, 2020
Data platforms decisions are critical for 5G era
So 5G, done right, offers a significant counter to almost every challenge they now face including lowering cost of service delivered, better spectrum utilization while opening new doors to new revenue streams in direct, indirect, and wholesale motions. The raw performance and flexibility of 5G will delight customers and serve as a foundation for vertical industry transitions like Industry 4.0 in the manufacturing sector.
That said, the back-end data platforms supporting new services in areas like IOT and enterprise, real-time charging and billing, network optimization, policy management, OSS, fraud detection must be able to keep up with the step-change in overall data volume, velocity, and veracity.
Investments that are made in these systems and foundation building blocks like NoSQL data platforms today will be expected to match the lifecycle of 5G and be built for peak 5G which isn’t expected for another 5 years. While these systems, including real-time charging and billing systems and customer management, aren’t necessarily the most exciting parts of 5G, they are nonetheless vital and if they perform poorly, customers will be let down, costs will rise, and the ROI of 5G will take a big hit.
For more information watch the webinar I delivered on this topic with John Shelnutt: How to Accelerate IoT and Real-Time Services with 5G and MEC




