Data Platforms in Financial Services – The NoSQL Edge Report
This article was originally published on www.gomedici.com/data-platforms-in-financial-services-nosql-edge-report-by-medici
The financial services industry acts as a force multiplier of economic activities, from storing to creating wealth and providing access to credit. It has always strived to evolve with the changing needs of the consumer, and the digitization of financial services has been an ongoing process for the past few decades. Financial services can no longer offer generic solutions that target a wide range of consumers. Be it an individual working in a multinational corporation or a student, a neighborhood business, or a large-scale enterprise catering to a global populace, each client’s needs are unique.
To address this diversity, institutions are consuming data from multiple sources inside and outside the enterprise. These include structured data from sources like enterprise systems, market systems, and government databases, as well as unstructured data from social networks and media.
In this article, we share some snippets from the Medici-Aerospike white paper on using NoSQL databases in financial services organizations. This report, prepared by MEDICI in partnership with Aerospike, focuses on sharing knowledge and promoting interest in NoSQL databases and exploring collaboration opportunities and business benefits derived from NoSQL databases, specifically for the financial services industry. This report also explores Aerospike’s vision of delivering informed and real-time decision-making for the financial services industry, with NoSQL-related case studies from Aerospike.
What to Expect From the Report
The report deep-dives in the following topics:
Application and criticality of data processing at scale in financial services, covering fraud prevention, personalized customer experience, challenges of data sources & formats and infrastructure requirements for instantaneous transactions
Highlights challenges associated with data processing in financial services
Data handling and processing in traditional architectures
NoSQL databases in the changing world of financial services covering digital transformation in financial services and the changes imposed by it
Preference of NoSQL over traditional databases
Opportunities and business benefits that can be derived from NoSQL databases
Common Data Processing Challenges in Financial Services
Dealing with data silos: Data in the financial organization is complex as it comes from different departments within the organization and multiple sources. These data silos pose a significant roadblock to making data-driven business decisions.
Limited or lack of real-time processing: In traditional architectures, processing data is largely batch-based. In financial services, better customer experience manifests through real time discovery of products and solutions, personalization, pricing, and adaptation of processes. However, traditional platforms are not designed for such highly scalable operations.
Performance and availability concerns: Mission-critical applications, especially consumer-facing apps, demand always-on availability. An increase in volumes coupled with the transition to distributed architectures has put the spotlight on performance and availability. There is a need to have modern ways of managing clustering and load balancing.
Inconsistent data: As modern architectures increasingly rely on non-relational databases and co-exist with relational databases, data integrity becomes a critical aspect of being taken care of. If there is dramatic data variation in terms of integrity, consistency, and structure, it limits the potential to make data-driven business decisions.
Difficult to transition beyond mainframes: Although mainframe systems’ stability is indisputable in processing, compliance, and settlement operations, few sophisticated workloads need to be moved to distributed real-time databases. NoSQL databases can process datasets that do not work well with relational systems.
Difficult to accommodate both structured and unstructured data: For machine learning models to work in real time, a continuous stream of data is essential. Historical data from multiple sources across the organization need to be combined and be subjected to ML algorithms on a real-time basis. This calls for highly scalable data stores and processing that can accommodate both structured and unstructured data.
One of the changes seen in financial institutions’ IT systems is the adoption of NoSQL databases.
What Is a NoSQL Database?
NoSQL is usually referred to as “not-only-SQL,” non-SQL, or non-relational databases. NoSQL databases such as key-value pairs are built for prime throughput versus relational databases with relative dependence. Using loose dependencies and quick indexes, NoSQL databases are perfect for streaming analytics and IoT applications because data can quickly be stored and referenced from multiple, disparate data sources.
NoSQL databases represent an approach to data management and database design that’s useful for extensive sets of distributed data. They encompass a good range of technologies and architectures, seeking to resolve the scalability and Big Data performance issues that relational databases were not designed to deal with. NoSQL is particularly useful when an enterprise has to access and analyze massive amounts of unstructured data or data stored remotely on multiple virtual servers within the cloud.
The report thoroughly examines what a NoSQL database is, its types, and how its adoption can help in the digital transformation of the financial services industry. Access the report here.
Opportunities and Business Benefits that Can Be Derived from NoSQL Databases
NoSQL databases have increased in popularity with the rise of Big Data-based applications. Compared to relational databases, NoSQL databases are much cheaper to scale, are capable of managing unstructured data, and better suited to the current agile development approaches. Modern, cloud-based NoSQL databases offer five essential advantages that transform the way banks operate and serve their customers:
Improved fraud prevention and financial crime monitoring: NoSQL databases enable real-time analytics on live transactions by removing the latency associated with moving data from operational databases to data warehouses for analytical processing.
Real-time digital ID validation: ID verification has gained increased significance in the global, digital world. Especially financial services companies have to ensure that ID fraud does not happen at various levels of interactions with customers and clients. The ID verification firms have to instantly make API calls to these databases and display the results in almost real-time. NoSQL databases reduce read latency in such situations and ensure that these organizations can handle real-time customer trust decisions virtually, thereby eliminating false positives and massively enhancing fraud detection.
Personalized offerings using improved real-time data analytics: Customers do not want generic products and services that cater to a broader population. Each individual’s financial requirements are different, and they expect their bank or any other financial institution to offer them solutions matching their needs. Companies need robust data management tools such as NoSQL databases to store and access these multiple sources. These will, in turn, enable the organization to make real-time analytics on user preferences and ensure that products and services are provided to cater to the specific needs of the customer.
Targeted marketing: Targeting marketing has become the most effective medium for brand engagement from social media sites, displaying ads based on viewer preferences to recommendation engines on streaming platforms and e-commerce sites. This is only possible through large-scale data crunching offered by NoSQL databases using data sourced from user profiles, cookies, and social media engagements. Managing massive amounts of audience segmentation data exchanges behind this transaction between players such as buyers, sellers, and ad exchanges requires low latency and efficient data management on the part of databases.
Pre-trade assistance: Another use case of the capability to support personalized experience is data analytics for trade decisions and risk assessment. Pre-trade assistance uses analytics to study information in real time from various sources, both highly structured market data, and unstructured news information & research. Instead of just displaying this data, real-time analytics can be performed using NoSQL databases that provide a holistic view of understanding a particular instrument.
Financial institutions are increasingly looking to move operational and delivery models from physical to digital platforms as more and more customers prefer these channels. NoSQL will play a critical role in enabling this shift and in ensuring the high quality of services that their new, digital clientele expects from them. Here, some NoSQL industry leaders, such as Aerospike, can be a valuable partner in the transformation story.
How Aerospike Helps
Traditional architectures call for a large DRAM-based cache in front of a persistent store for high throughput and extremely low latency over large volumes of data. By contrast, Aerospike’s Hybrid Memory Architecture™ (HMA) offers a fundamentally different approach. By persisting data on fast SSD devices and leveraging primary key indexes (whether in DRAM, SSD, or Intel® Optane™ DC Persistent Memory), many advantages are realized without compromising performance while adding persistence, correctness, and security.
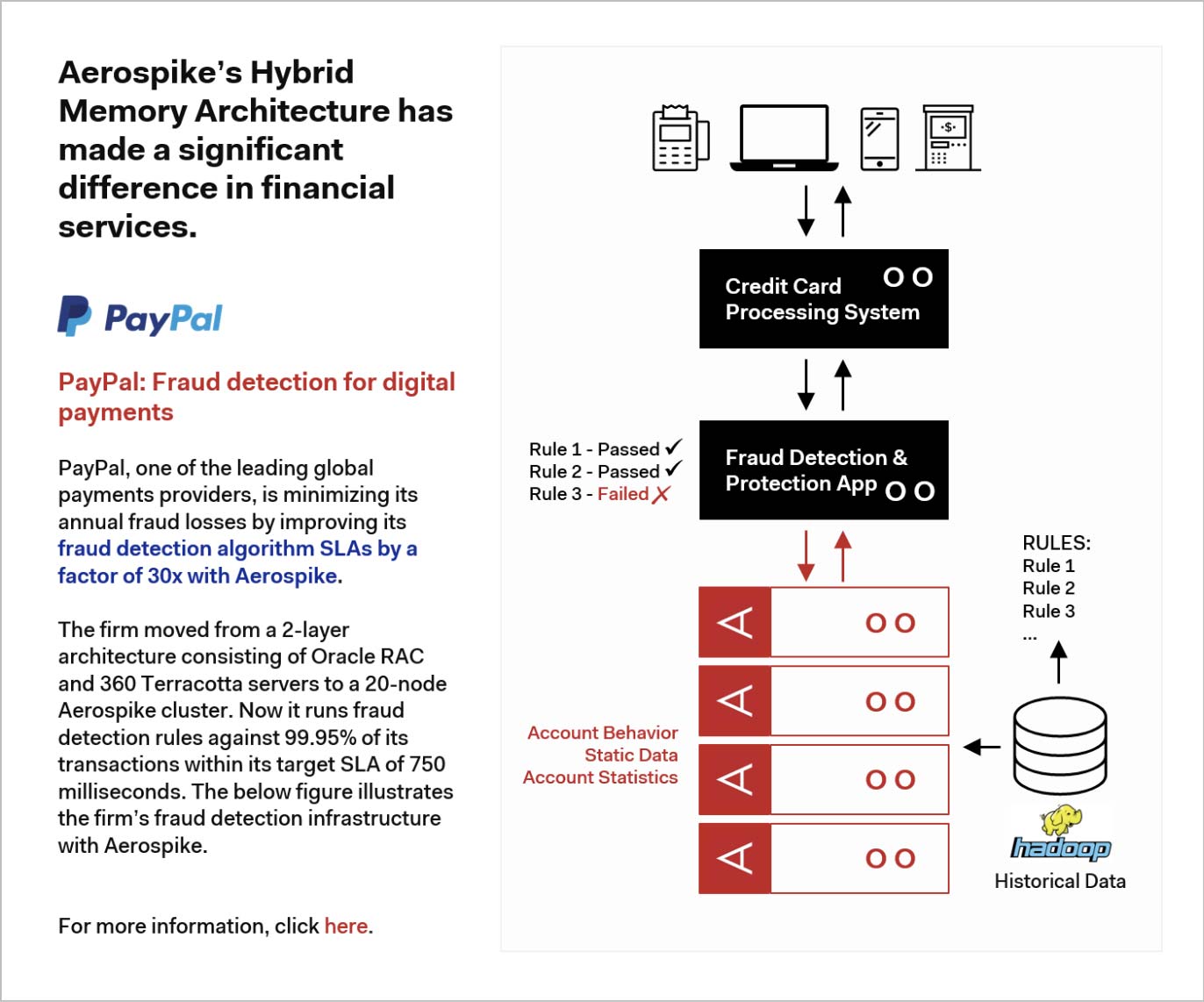
The technology shared in the use case empowers organizations to fight fraud instantly, increase shopping cart size, deploy global digital payment networks, and deliver one-to-one personalization for millions of customers.
Aerospike’s global line-up of customers includes Airtel, DBS Bank, Nielsen, PayPal, Snap, Verizon Media, and Wayfair. The company is headquartered in Mountain View, Calif., with additional locations in London, Bengaluru, and Tel Aviv.
Conclusion
Technology is going to play a massive part in this rapidly changing financial services business environment. Customers who are accustomed to instant updates through social media will expect a similar service from their financial service providers. This is only possible by removing constraints posed by traditional architectures that have existed over the years. Traditional databases are struggling to cope with the massive influx of data from multiple sources and multiple formats. On the other hand, NoSQL databases bring immense value when an enterprise has to access and analyze massive amounts of unstructured data or data that is stored remotely on virtual servers within the cloud.
Financial services have traditionally been innovators in technology. However, the baton has passed on to other areas in recent times, and the industry has struggled to cope with customer expectations. Innovations such as cloud and business analytics are yet to realize their full potential at scale in the industry. Modern, cutting-edge platforms such as NoSQL databases will help accelerate innovation to achieve its full potential so that the industry meets its consumers’ demands and expectations.
Grab your copy of the full White Paper here




