Flexible storage
With Aerospike’s flexible storage, you control the media that stores data, the primary index, and secondary indexes.
Storage media
Storage media for data or indexes includes:
- Dynamic random access memory (DRAM), which we refer to as memory.
- Non-volatile memory extended (NVMe) Flash, AKA solid state drives (SSDs).
- Intel Optane™ Persistent Memory (PMem).
Flexible storage configurations
-
Hybrid memory architecture (HMA) is Aerospike’s default configuration where the primary index is stored in memory, and data is stored on the SSD.
-
The In-Memory configuration stores the index and the data in DRAM. Optionally, data can be backed to NVMe-compatible storage or filesystem.
-
The All Flash configuration stores the index and the data in Flash. All Flash is only available in Aerospike Enterprise Edition (EE).
The following diagram illustrates Aerospike’s flexible storage configurations.
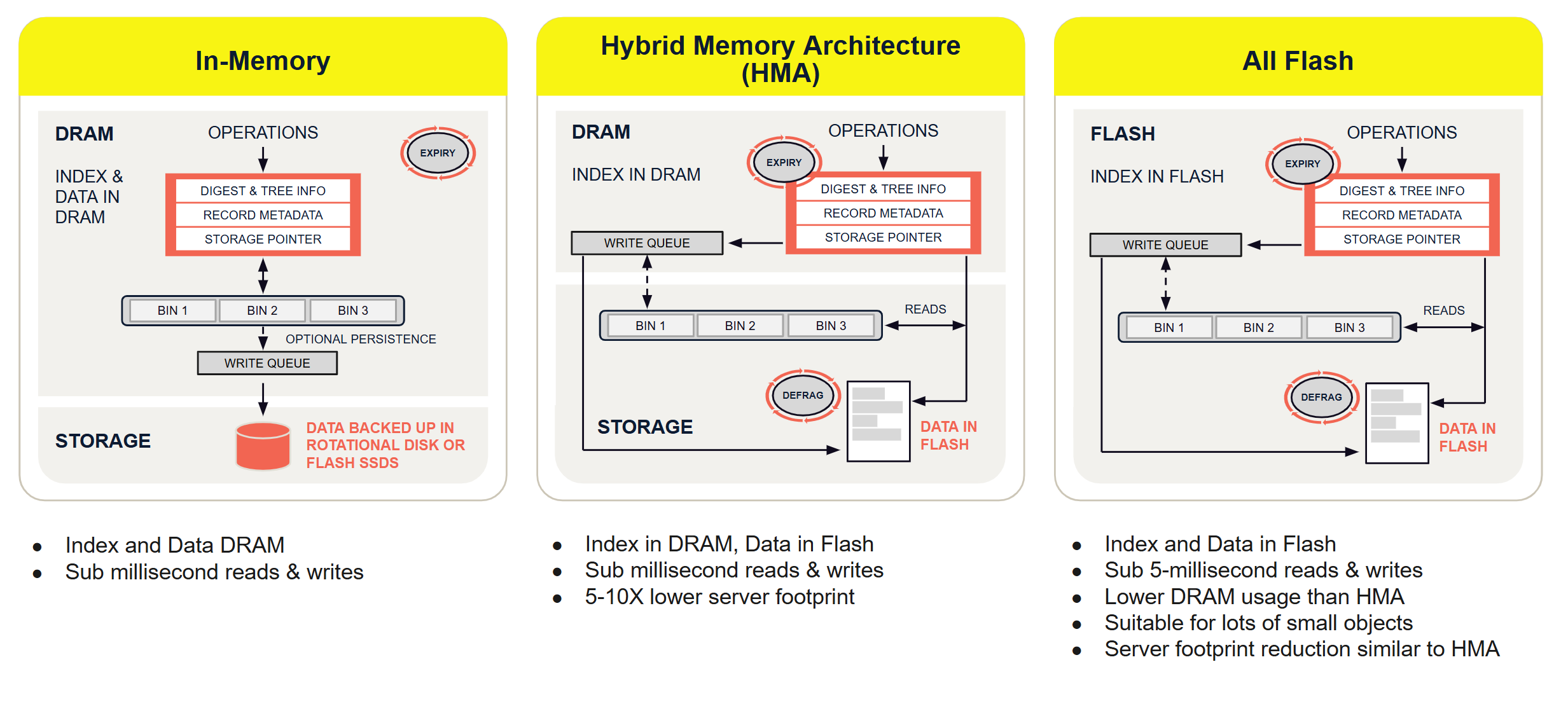
Figure 1: Flexible storage options
Namespaces, records, and storage
Each namespace can have a different storage configuration. For example, you can configure small, frequently accessed namespaces in memory and put larger namespaces in less expensive, high performance SSDs.
In Aerospike:
- Record data is stored contiguously.
- A record can be as large as 8MiB.
- New record versions are always copy-on-write persisted.
- Free space is continuously reclaimed through defragmentation.
- Each namespace has a fixed amount of storage, each node gets an equal distribution of data, and requires the same amount of storage as other cluster nodes.
Aerospike achieves high reliability by storing multiple copies of each record. Since Aerospike automatically reshards and replicates data on failure or during cluster node management, k-safety is maintained at a high level.
Aerospike uses random data distribution to keep data unavailability very small when several nodes are lost. For example, in a 10-node cluster with two copies of the data, if two nodes are simultaneously lost, the amount of unavailable data before replication is approximately 2% or 1/50th of the data.
The Aerospike defragmenter tracks the number of active records on each block in data storage and reclaims blocks that fall below a minimum level of use.