RBAC for Aerospike Graph Service
Overview
This page describes how to set up Role Based Access Control (RBAC) for the Aerospike Graph Service (AGS) using Java Web Tokens (JWTs).
We recommend using RBAC on a secure network connection between client applications and AGS.
Multi-tenant graph support
If your AGS instance uses multi-tenant graphs, you can create JWTs that assign different roles to different graphs by specifying a graph name in your role definition. See the Create JWTs section of this page for details.
Enable RBAC
Enable RBAC for your AGS instance with the following configuration options:
| Option | Required? | Value |
|---|---|---|
aerospike.graph-service.auth.jwt.secret | yes | Any string that you choose. |
aerospike.graph-service.auth.jwt.issuer | yes | Your organization or a third-party authentication service. |
aerospike.graph-service.auth.jwt.algorithm | no | One of: HMAC256, HMAC384, HMAC512. Default is HMAC256. |
After RBAC security is enabled, all connections with AGS must carry a Java Web Token (JWT) with the correct secret and issuer, and all users must have sufficient privileges to run their queries.
Authentication details
- When authentication is enabled, the
evaluationTimeoutparameter is ignored when it is part of Gremlin queries. - To use the
evaluationTimeoutparameter when authentication is enabled, set it globally with theaerospike.graph-service.evaluationTimeoutoption in your properties file.
Roles
Role access levels in AGS include:
READ
Can read data. No write or admin privileges.
The following commands are blocked for READ users:
| Blocked Gremlin steps |
|---|
addV |
addE |
drop |
mergeE |
mergeV |
property |
| Blocked call steps |
|---|
aerospike.graph.admin.rbac-jwt.issue-token |
aerospike.graph.admin.index.drop |
aerospike.graph.admin.index.create |
aerospike.graphloader.admin.bulk-load.* (all bulk-load steps are blocked) |
READ_WRITE
Can read data and perform write operations such as addV(), addE(), and property().
All Gremlin steps are available to READ_WRITE users. The following
commands are blocked:
| Blocked call steps |
|---|
aerospike.graph.admin.rbac-jwt.issue-token |
aerospike.graph.admin.index.drop |
aerospike.graph.admin.index.create |
ADMIN
Can perform read and write operations, plus create and delete indexes. No Gremlin steps or call steps are blocked.
Create JWTs
Use the following procedure to create JWTs for use with graph authentication.
- Create the
ADMINJWT
An admin user first creates a token with admin-level privileges. The first admin token must be created using an external token authority.
jwt.io provides a free utility for generating JWTs.
-
Select an algorithm from the dropdown menu. Valid algorithms for use with AGS are:
- ‘HS256’ (corresponds to ‘HMAC256’)
- ‘HS384’ (corresponds to ‘HMAC384’)
- ‘HS512’ (corresponds to ‘HMAC512’)
The
HEADERfield auto-populates based on your choice. -
Fill in the
PAYLOADfield with the following, edited to suit your needs.If your AGS instance does not use multi-tenant graphs, the
rolefield contains only the specified role. If your AGS instance uses multi-tenant graphs, therolefield may contain:- A list of key-value pairs with the graph name and the role for that graph.
- A single role that applies to all graphs.
The following example shows the
PAYLOADfield for an AGS instance without multi-tenant graphs:Terminal window {"iss": "jwt.io","iat": 1717107890,"exp": 14210121600,"aud": "","sub": "admin","role": "ADMIN"}The following example shows the
PAYLOADfield for an AGS instance with graphs namedGraphAandGraphB:Terminal window {"iss": "jwt.io","iat": 1717107890,"exp": 14210121600,"aud": "","sub": "admin","role": {"GraphA" : "ADMIN", "GraphB" : "READ_WRITE"}} -
Add your secret to the
VERIFY SIGNATUREfield, and the encoded token on the left side is ready to use.
The following diagram shows the procedure for creating a token with an external token issuer:
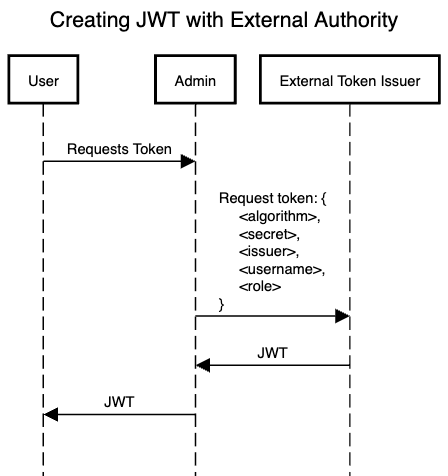
- Create subsequent JWTs using admin token
The admin user can create tokens for other users, including admin tokens. Other users can use their tokens for graph queries, and the issuer and secret credentials are not required with the application code.
The following diagram shows the procedure for creating a token
with the AGS
aerospike.graph.admin.rbac-jwt.issue-token command:
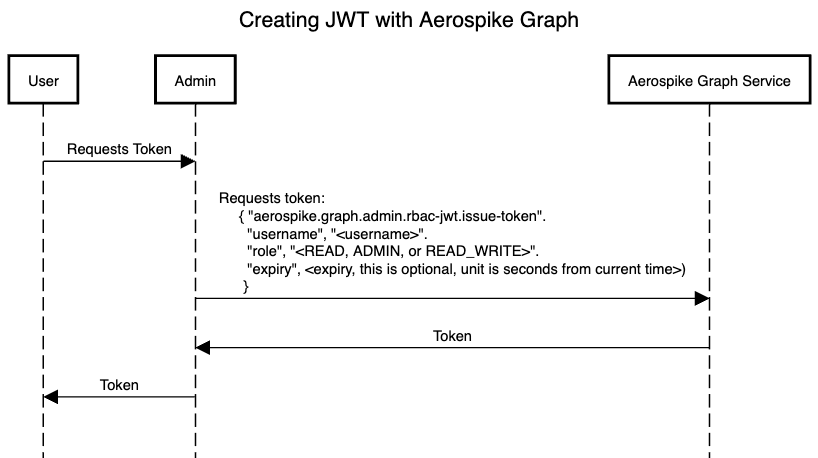
- The admin user can create tokens with the Gremlin call step
aerospike.graph.admin.rbac-jwt.issue-token. Provide the new token’s username and intended role as parameters:
g.call("aerospike.graph.admin.rbac-jwt.issue-token") .with("username", "<USERNAME>") .with("role", "<ROLE>") .next()Connect to AGS using a JWT
The following diagram shows the procedure for connecting to AGS with a JWT:
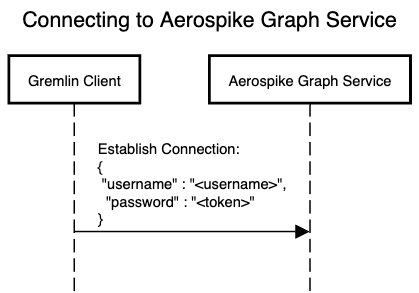
Using a JWT over a Gremlin server connection
The following Java code example demonstrates a Gremlin server login with a JWT:
final Cluster cluster = Cluster.build() .addContactPoint("localhost").port(8182) .credentials(<USERNAME>, <TOKEN>) .create();Using a JWT over an HTTP connection
To authenticate an HTTP connection with a JWT, set the
Authorization property to Bearer <JWT>, where <JWT>
is a base64 encoded string of a JWT.
The following Java code example demonstrates setting up an HTTP connection with a JWT:
public String adminIndexListHeaders(final String userCredentials) { try { final URL url = new URL("http://localhost:9090/admin/index/list"); final HttpURLConnection con = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
// Send request to the server and read reply final String token = "Bearer " + new String(Base64.getEncoder().encode(userCredentials.getBytes()));
// Send request to the server and read reply con.setRequestMethod("GET"); con.setRequestProperty("Authorization", token);
// Read input stream into String final byte[] bytes = con.getInputStream().readAllBytes(); final String response = new String(bytes); return response; } catch (final Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } }