Aerospike Graph architecture
Aerospike Graph is a distributed, high-performance graph database architected for real-time, large-scale workloads where predictable performance and operational efficiency are non-negotiable. Built atop Aerospike Database, it combines the flexibility and ease of use of a graph-native query language (Gremlin) with the performance, resilience, and resource efficiency of the Aerospike database.
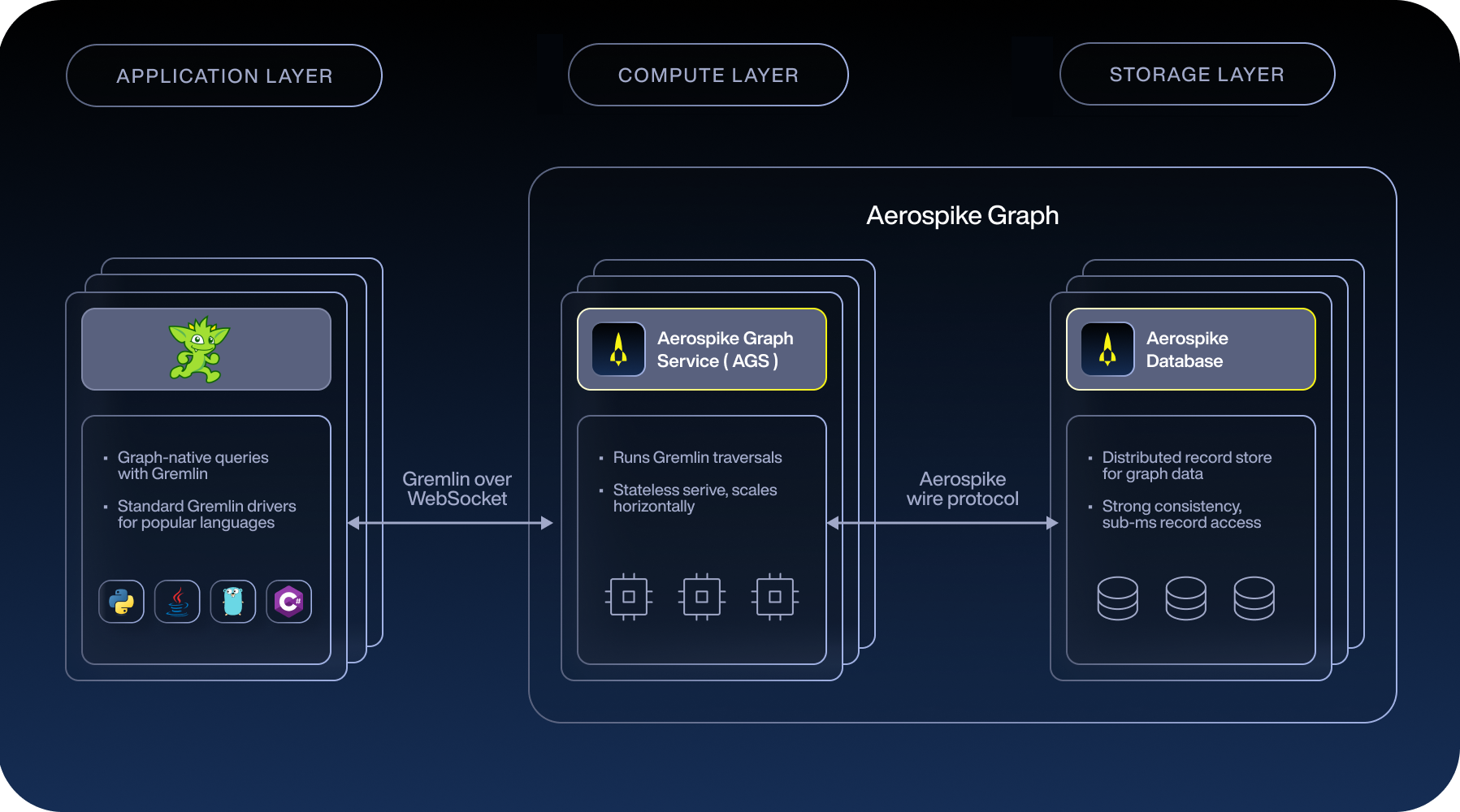
A layered architecture separates compute from storage, allowing each to scale independently based on workload demands.
Application layer
Applications interact with Aerospike Graph using the Apache TinkerPop Gremlin query language. Standard Gremlin drivers are available for popular languages such as Java, Python, Go, and .NET.
Applications submit Gremlin traversals to AGS over WebSocket, enabling language-agnostic access to the graph while keeping application logic independent of storage and execution details.
Compute layer: Aerospike Graph Service (AGS)
AGS provides a graph-native interface through the Gremlin query language, implementing the Apache TinkerPop framework. It processes Gremlin queries with deep integration with Aerospike Database and incorporates specialized query optimizations (including step reordering, server-side filtering, and parallel execution) for high-performance traversal processing.
Because AGS is fully stateless:
- Any AGS instance can serve any request
- Instances scale horizontally with no coordination overhead
- Throughput can be increased or reduced without downtime or data migration
This enables linear scaling of query throughput while maintaining consistent performance across dynamic workloads.
Storage layer: Aerospike Database
Graph elements (vertices, edges, properties) are stored in Aerospike Database using an optimized data model.
This data model ensures:
- Predictable sub-millisecond read and write latencies
- Strong consistency
- Automatic sharding and distribution across cluster nodes
This combination enables efficient storage and graph traversal operations over billions of graph elements with consistent low-latency access at any scale.
Query execution flow
The following steps describe how a Gremlin query is processed across the layers:
- An application submits a Gremlin traversal using a standard Gremlin driver.
- AGS receives the traversal over Gremlin over WebSocket and begins execution.
- Traversal steps retrieve or mutate graph elements stored in Aerospike Database using the Aerospike wire protocol.
- AGS processes intermediate results and returns the final traversal result to the application.