Deploy in Starburst Enterprise Platform on AWS
These instructions describe how to deploy the Aerospike Trino connector in Starburst Enterprise on AWS. Starburst Enterprise is an enterprise-ready distribution of open source Trino (formerly PrestoSQL).
The Aerospike connector does not support the following Starburst Enterprise features:
- Materialized Views
- Caching Service
- Atlas Integration
- Data Catalog - AWS Glue and Hive Metastore
Prerequisites
- A valid Starburst Enterprise license
- Python 3.8
- Java SE 11
- Verify the Trino version in the Starburst Enterprise release that you plan to use. For information on the corresponding connector release, see Deploying the Trino Connector and a Trino Cluster on Bare Metal or in VMs.
Provision EC2 instance
-
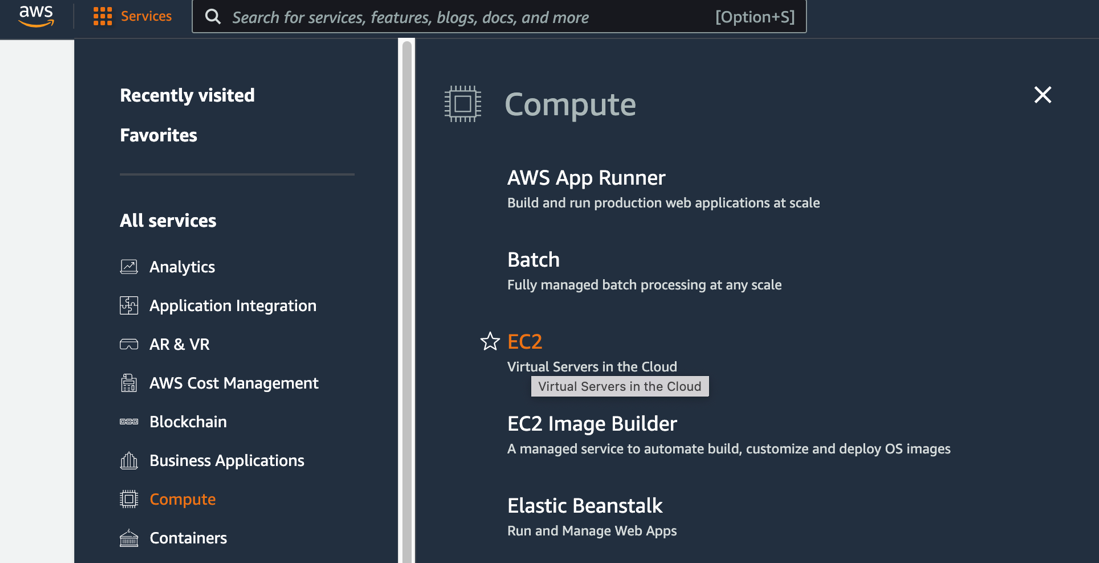
Log into the AWS Management Console, then select Services > Compute > EC2.
-
Select Launch Instances.
-
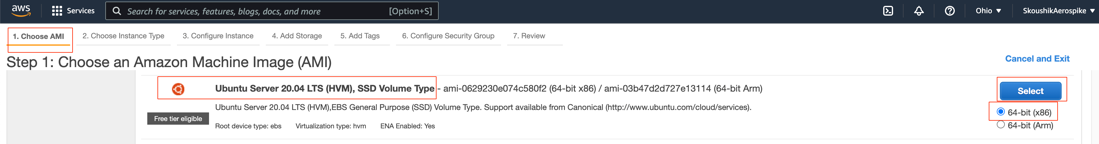
Select AMI > Ubuntu Image 20.04 XXX > 64 Bit(X86) > Select.
-
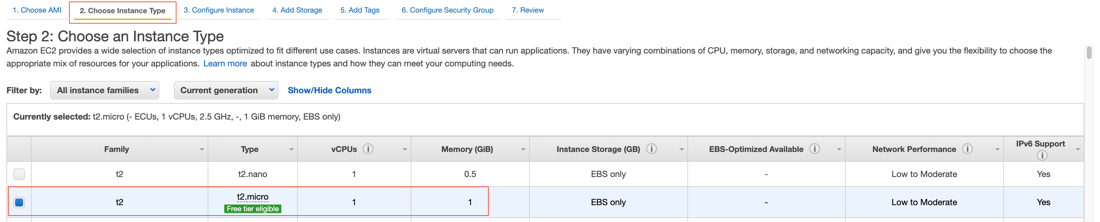
Select Choose Instance Type > t3.2xlarge.
-
Select Next: Configure Instance Details.
-
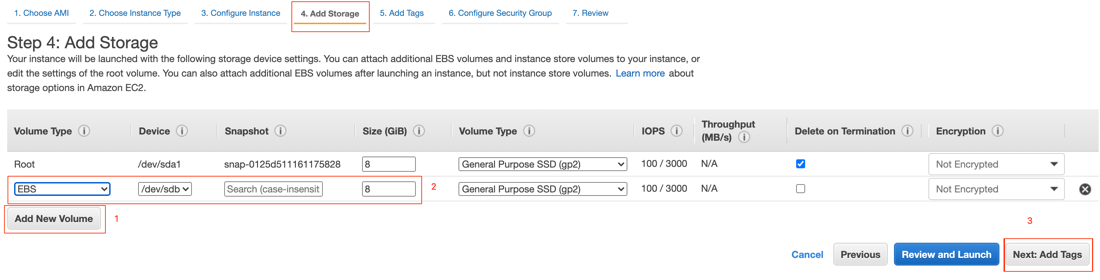
Go to Add Storage > Add New Volume and check the specified settings. When you have confirmed the settings, click Next: Add Tags.
-
Choose Add Tags > Add Tag then enter the appropriate value for Key and Value. For example,
DevelopmentandStarburst_Node_Dev_XorQAandStarburst_Node_QA_X.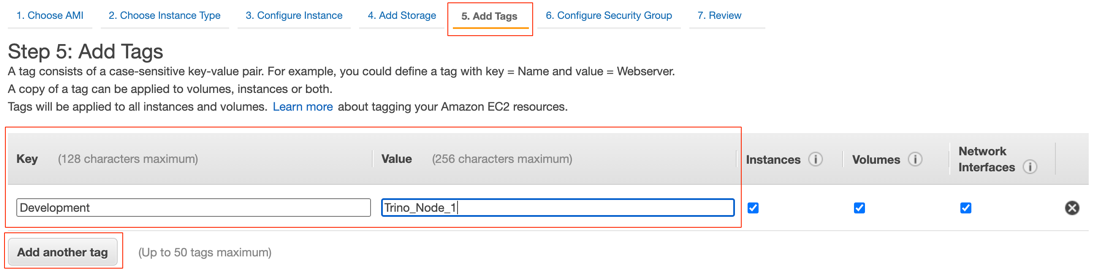
-
At the bottom of the screen, click Next: Configure Security Group.
-
If you need ports other than SSH, like port 8080 or 3000-3003, select Configure Security Group > Add Rule. Add rules to allow the necessary ports.
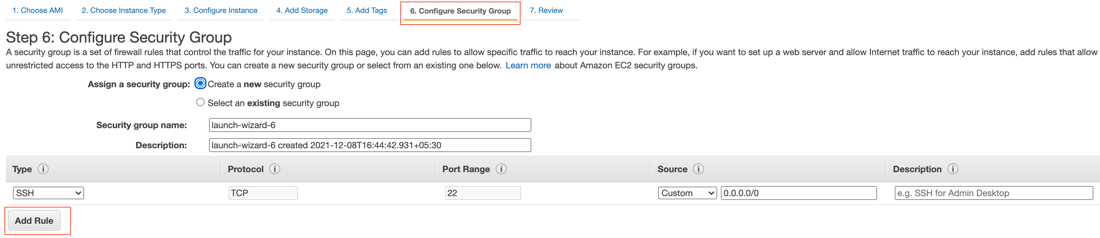
-
Click Review and Launch.
-
Review the settings, then click Launch.
-
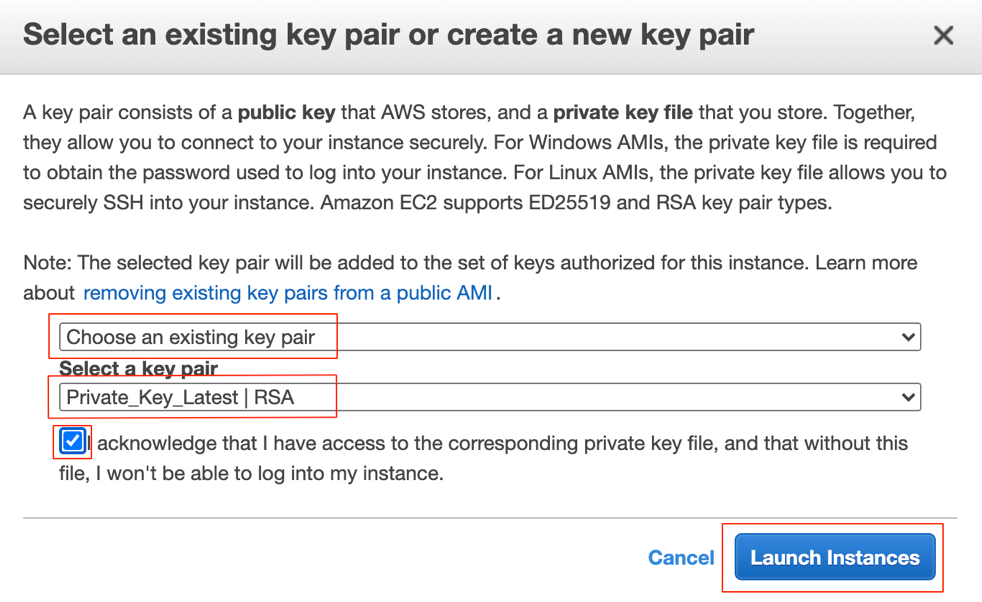
Select one of the options:
- Choose an existing key pair
- Create a new key pair
- Proceed without a key pair
If existing keys are available, select Choose an existing key pair, select the Public/Private key, tick the box to confirm you have access, then click Launch Instances.
Deploy Starburst and Aerospike
Pick the public IP address of the recently-created instance before proceeding to the next steps from the AWS console. For the following examples, we assume the IP address is 192.0.2.0.
-
Use PuTTY (Windows) or Terminal (Mac) to log into the configured instance.
ssh -i ~/Downloads/Private_Key_Latest.pem ubuntu@192.0.2.0 -
Install Java and Python, if they are not pre-configured on your instance.
sudo apt updatesudo apt-get install openjdk-11-jdksudo apt install python3.8 -
Download Starburst Enterprise LTS version.
-
Upload it to the
/home/ubuntudirectory on your instance. -
Go to the
/home/ubuntudirectory on your instance and install UUID.cd /home/ubuntusudo apt-get install uuid -
Run the UUID command and capture the node ID for
node.properties.uuid -
Upload all relevant files to the
home/ubuntudirectory, including the following:- A valid Starburst Enterprise license.
- The Starburst Enterprise download in
.tar.gzformat.
-
Make the
/etc/sepdirectory and copy over your license key.sudo mkdir -p /etc/sepcd /etc/sepsudo cp /home/ubuntu/*.license . -
Move to the
/home/ubuntudirectory, then uncompress the Starburst installation package.cd /home/ubuntutar xvfz starburst-enterprise-370-e.1.tar.gz -
Move the uncompressed Starburst file to
/opt/starburst, then go to that directory and create a symlink.sudo mv starburst-enterprise-370-e.1 /opt/starburstcd /opt/starburstsudo ln -s /etc/sep etc -
Go to the
/opt/starburst/plugindirectory and make a directory for Aerospike.cd /opt/starburst/plugin/sudo mkdir aerospike -
Copy all the JAR files from the Aerospike Trino Connector download into the new
/opt/starburst/plugin/aerospikedirectory. -
Create a
/var/trino/datadirectory and give it read/write/execute permissions for all users.mkdir -p /var/trino/datasudo chmod 777 /var/trino/data -
Move into the
/etc/sepdirectory and edit thenode.propertiesfile./etc/sepsudo vi node.properties -
Set the following configurations. For
node.iduse the UUID you captured previously with theuuidcommand.node.environment=productionnode.id=XXXXXXXXXXXX ## UUID captured previouslynode.data-dir=/var/trino/data -
Save and exit the file.
-
Edit
jvm.config.sudo vi jvm.config -
Configure Trino in Starburst Enterprise. For more information, see Configuring Trino.
Here’s a sample configuration:
-server-Xmx16G-XX:-UseBiasedLocking-XX:+UseG1GC-XX:G1HeapRegionSize=32M-XX:+ExplicitGCInvokesConcurrent-XX:+ExitOnOutOfMemoryError-XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError-XX:-OmitStackTraceInFastThrow-XX:ReservedCodeCacheSize=512M-XX:PerMethodRecompilationCutoff=10000-XX:PerBytecodeRecompilationCutoff=10000-Djdk.attach.allowAttachSelf=true-Djdk.nio.maxCachedBufferSize=2000000 -
Save the file and exit.
-
Edit
config.properties.vi config.properties -
Set the cluster configurations, using one of the two following options.
Option 1: Single-Node Deployment
coordinator=truenode-scheduler.include-coordinator=truehttp-server.http.port=8080query.max-memory=50GBquery.max-memory-per-node=1GBdiscovery.uri=http://[coordinator node IP address]:8080Option 2: Multi-Node Deployment
If you plan to use one or more worker nodes, one set of configurations applies to the coordinator node, and a second set applies to each worker node.
On the coordinator node:
coordinator=truenode-scheduler.include-coordinator=truehttp-server.http.port=8080query.max-memory=50GBquery.max-memory-per-node=1GBdiscovery.uri=http://[coordinator node IP address]:8080On each worker node:
coordinator=falsequery.max-memory=50GBquery.max-memory-per-node=1GBdiscovery.uri=http://[coordinator node IP address]:8080 -
Save and exit the
config.propertiesfile. -
Edit
log.properties.sudo vi log.properties -
Set the following configuration:
io.trino=INFO -
Save the file and exit.
-
Create a
catalogdirectory and move into it.sudo mkdir catalogcd catalog -
Create a file named
aerospike.properties.sudo vi aerospike.properties -
Set your configurations. For available settings, see Configuration Properties for Aerospike Connect for Trino.
Example configuration file:
connector.name=aerospikeaerospike.hostlist=xx.xx.xx.xx:3000,yy.yy.yy.yy:3000,zz.zz.zz.zz:3000## aerospike node listaerospike.split-number=8aerospike.strict-schemas=falseaerospike.record-key-hidden=falseaerospike.enable-statistics=trueaerospike.insert-require-key=trueaerospike.table-desc-dir=/etc/trino/aerospikeaerospike.clientpolicy.tls.enabled=false -
Save the file and exit.
By default, the Trino connector uses heuristics to rapidly infer schemas without the need for you to specify them. However, you can choose to specify the schema by creating a table definition. For more information, see Specifying Trino Schemas.
-
Go to
/usr/binthen run the Starburst launcher.cd /usr/binpython3 /opt/starburst/bin/launcher.py run
-
Watch the Server Started messages and troubleshoot any errors.
Although we have tested connecting to Starburst Enterprise with DBeaver, we encourage you to try out other Starburst clients based on your needs.
For additional information on how to develop SQL queries to generate insights from Aerospike data, see the following: