Recommendations for Microsoft Azure
OS
We recommend using the latest Ubuntu Server LTS as it has the most recent optimizations and bug fixes on Azure. You can find Ubuntu through the Azure portal or at this page.
Instance type
Lsv2 family of VMs are specifically designed for high performance IO applications and is the primary recommendation of Aerospike.
However, the M and DSv2 can also be utilized should their characteristics match your usage.
In general, any persistence based storage should utilize VM families with the ‘S’ suffix. This indicates the VMs have Premium (SSD) Storage support.
Network setup
By default, machines within the same Virtual Network in Azure can communicate freely with each other. Aerospike uses TCP ports 3000 for communication with clients and 3002-3003 for intra-cluster communication. These ports need not be open to the rest of internet. If the database clients are present within the same Virtual Network, there should not be any need for a separate firewall rule, as they will be able to connect over port 3000.
You will need a port for SSH access to your instances (default tcp port 22).
All instances in Azure are assigned an internal IP address. These internal IP addresses should be used in the mesh heartbeat configuration.
Persistent disks
Azure provides storage in the form of VHD Disks in Storage Accounts.
There are two types of disks. High performance Premium Storage offers SSD backed storage, while Standard Storage offers HDD backed storage. The performance of the disk is closely tied to the size of the disk volume.
Local SSD
Some Instance types come with local SSDs. This provides extremely good performance, with high input/output commands per second (IOPS) and low latency compared to the persistent disk options. However, these local SSDs are created and destroyed along with the virtual machine instance. In spite of this, the local SSD storage option can be used judiciously with an Aerospike cluster so that the data is always replicated on multiple local SSDs attached to multiple virtual machines in the cluster.
Here is an example configuration snippet:
storage-engine device { device /dev/sdb }Local SSD IOPS are not limited by the persistent Disk IOPS allocations, nor instance IOPS allocations. They have their own allocations.
Shadow device configuration
As noted above, some Azure instance types have local SSDs. These can be significantly faster than Premium Storage Disks, as they are network attached. But Azure treats local SSDs as cache and not suitable for long-term data, as these volumes are purged when the instance stops.
To take advantage of local disks with the persistence guarantee of Azure Blob Storage, Aerospike has the Shadow Device configuration for the storage engine.
The write throughput is still limited by the instance limit and storage volume, sov this strategy gives good results when the percentage of writes is low.
An example config would be as follows:
storage-engine device{ device /dev/sdb /dev/sdc ... }Fault tolerance
Azure has the concept of Availability Sets. It consists of Update Domains and Fault Domains.
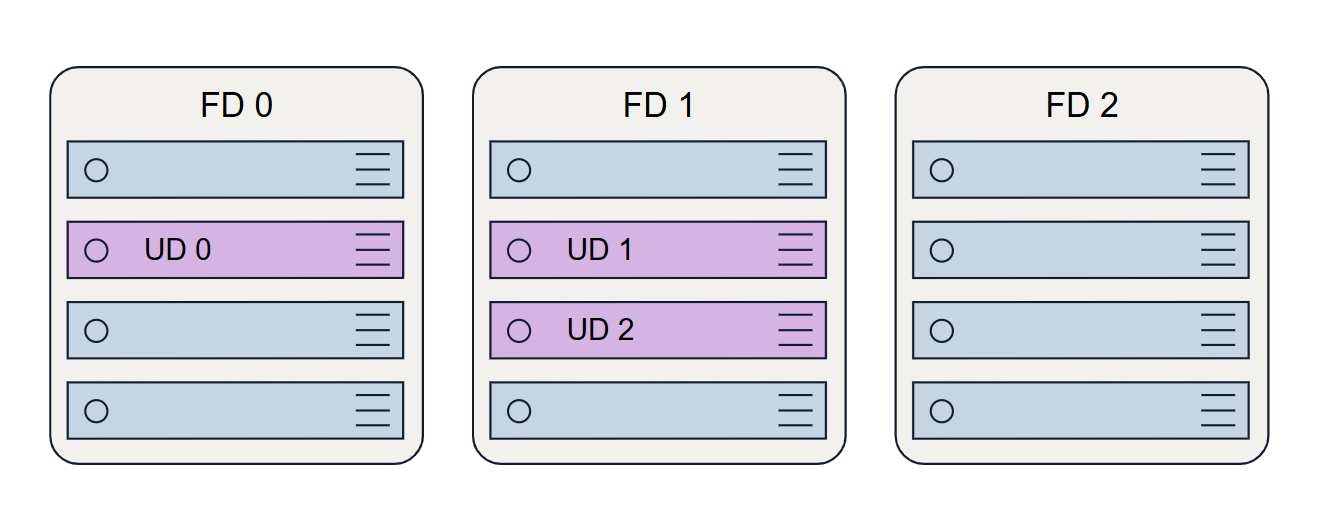
Update Domains are groups of physical systems that can be rebooted simultaneously in a maintenance event.
Fault Domains are groups of physical systems that share power and network switch.
Azure will not give notice of VM reboots for Update Domain interruptions.
Aerospike also provides XDR replication in our Enterprise Edition to facilitate DR scenarios