Aggregation
Use Aerospike Stream UDFs to aggregate query results in a distributed fashion. The Aerospike aggregation framework allows fast and flexible query operations. This programmatic framework is similar to a MapReduce system, in that an initial map function runs over a collection and emits results in a highly parallel fashion. Results traverse a pipeline of either subsequent map steps or reduction steps and aggregation steps.
Unlike Hadoop or other frameworks using Java, Aerospike aggregation is implemented using Lua. Each client sends an aggregation request to all servers in the cluster, which independently count the results and return individual results to the requesting client.
The Aerospike aggregation framework differs from other systems because Aerospike recommends running aggregation against an index; this is essentially a where clause. Filtering against an index maintains high performance. Aerospike supports aggregation for tables and the entire namespace. The client then runs a final reduce phase, also in Lua, to sum results.
Use cases
-
Implementing aggregate functions such as SUM, COUNT, MIN, and MAX as user defined stream UDFs.
-
Real-time dashboarding: Using secondary indexes on a bin with an update time, aggregations quickly gather statistics on recently changed records. Aerospike aggregation touches fewer records compared to standard MapReduce systems, which act on the entire unindexed dataset.
Performing Aggregation
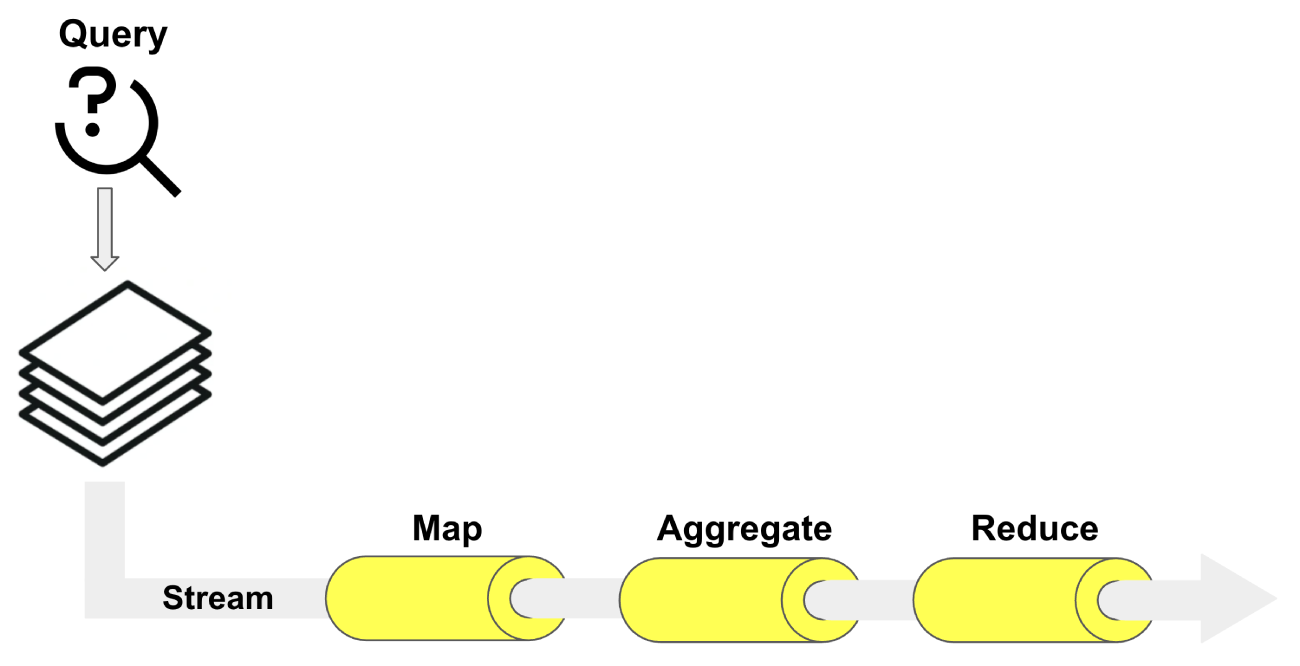
Figure 1: Aggregation flow
To implement aggregation in your application:
- Create a query application.
- Create indexes on a bin.
- Insert a record in an indexed bin.
- Create an aggregation module in Lua.
- Set the aggregation module path.
- Register the module with the Aerospike cluster.
- Construct an aggregate query with a predicate (
whereclause).
AQL
This aggregation process uses the aql command line tool.
-
Create an index.
The following example script creates a string index on the
user_profilenamespace,westset, andlocationbin. These examples use the in-memory storage engine. Queries can also run in on-disk namespaces.Create index Admin+> manage sindex create string ix2 ns user_profile set west bin locationUse 'show sindex' to confirm ix2 was created successfully.Add user_profile namespace user_profile {replication-factor 2storage-engine memory} -
Insert data.
Insert data aql> INSERT INTO user_profile.west (PK,location,last_activity) VALUES ('cookie_100','MA',342)OK, 1 record affected.aql> INSERT INTO user_profile.west (PK,location,last_activity) VALUES ('cookie_101','AZ',345)OK, 1 record affected.aql> INSERT INTO user_profile.west (PK,location,last_activity) VALUES ('cookie_102','CA',345)OK, 1 record affected.aql> INSERT INTO user_profile.west (PK,location,last_activity) VALUES ('cookie_103','AL',340)OK, 1 record affected.aql> INSERT INTO user_profile.west (PK,location,last_activity) VALUES ('cookie_104','TX',347)OK, 1 record affected.aql> INSERT INTO user_profile.west (PK,location,last_activity) VALUES ('cookie_105','MA',323)OK, 1 record affected. -
Create an aggregation module.
The following Lua code example counts the number of users in a location, using map-reduce instead of an aggregation step. The
aggregatefunction is more efficient, but map-reduce is more flexible.file: aggregate.luafunction count(s)function mapper(rec)return 1endlocal function reducer(v1, v2)return v1 + v2endreturn s : map(mapper) : reduce(reducer)endWhere the stream operations are:
mapper: Returns an integer (1) for each profile record.reducer: Adds all 1s for a total count.
-
Set the aggregation module path.
You must set the aggregation module path on the client side because the final reduce phases run on the client side after a response is returned from all cluster nodes. Use
aqlto set the relative path to the Lua aggregation module.The following example
aqlscript sets the path. aggregate.lua is in/home/user/lua_code.aqlstarted in/home/user.Terminal window aql> set LUA_USERPATH 'lua_code' -
Register the module with the cluster.
Terminal window aql> register module 'lua_code/aggregate.lua'OK, 1 module added. -
Construct the aggregate query.
Terminal window aql> AGGREGATE aggregate.count() ON user_profile.west WHERE location='MA'+-------+| count |+-------+| 2 |+-------+1 row in set (0.007 secs)